Chapter 1: The Spark
In late 2024 we met a forward-thinking fintech team. Their vision was clear: allow everyday investors in the UK and Europe to dive into U.S. stocks and ETFs with minimal friction—no clunky broker sign-up, no full brokerage build-out—just a seamless mobile or web experience. Even better: allow users to invest modest amounts (fractional shares), show their portfolio in GBP/EUR, and deliver real-time updates.
They came to us and said: “We want to build investing—but fast, elegant, and for the local currency user.” At INSART we said: “We can build the rails.” Because the heavy lifting behind brokerage—account-opening, custody, clearing—is enormous. Instead, we chose a partner: Alpaca Broker API, which offers a full brokerage rails stack: account-opening, funding, trading, events and more.
From day one our thinking was: the fintech client owns the UX, brand, growth engine; INSART builds the service layer, architecture, integration, resilience, compliance. The goal: launch in months, not years; deliver fractional investing, multi-currency display, real-time experience; build a foundation for scale and expansion.
Chapter 2: Mapping the Journey
We kicked off with a full-day workshop: product, UX, engineering, compliance. We plotted key user stories like a storyboard:
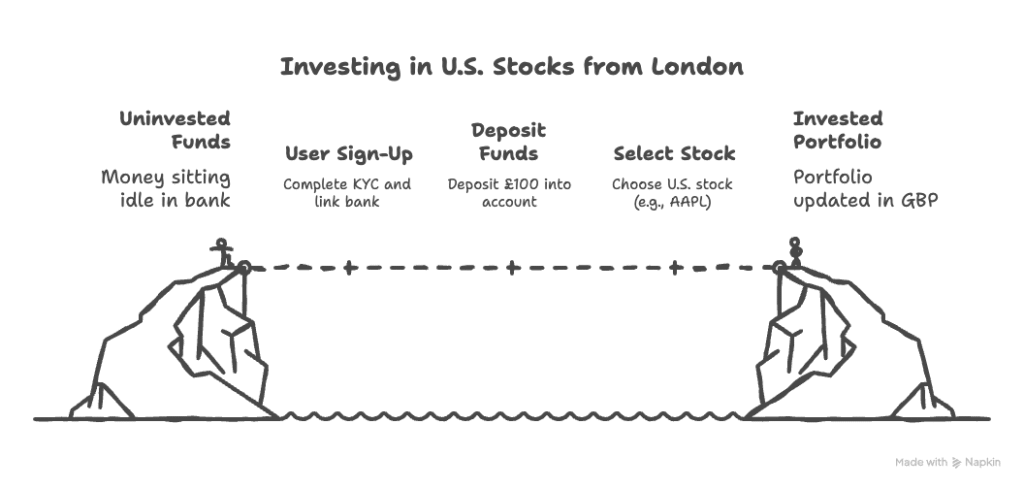
A user in London signs up → completes KYC → links their UK bank account → deposits £100 → selects a U.S. stock (say AAPL) → invests £25 as a “slice” → sees their portfolio update in GBP with a dynamic FX rate → gets notified when the order executes.
On the backend: our services handle user identity, map to a brokerage account under Alpaca, convert currencies, place orders via Broker API, listen to events, mirror portfolio, display to user.
We defined non-functional priorities early: latency targets (<2s from user tap to order execution notification), ability to scale to 100 k+ users in 12 months, currency conversion layer (USD ↔ GBP/EUR), fractional support, audit logs, multi-asset future (crypto, options). We also insisted on modular design: the brokerage wrapper must be abstracted so that if we ever swap or add rails, business logic remains stable.
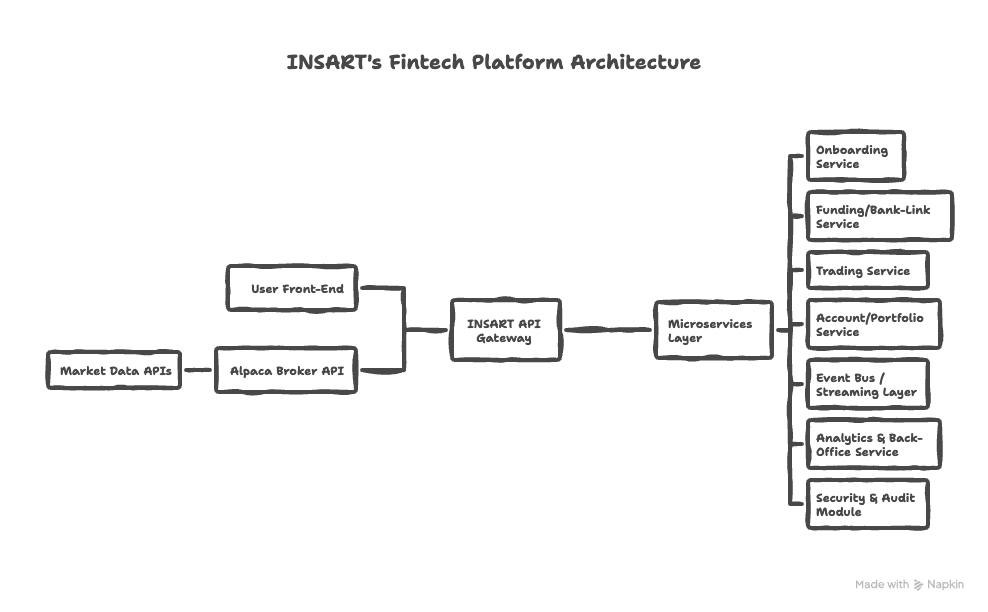
We then designed architecture:
User Front-End (Mobile/Web)
↕ (REST + WebSocket)
INSART API Gateway
↕
Microservices Layer:
├ Onboarding Service
├ Funding/Bank-Link Service
├ Trading Service (Broker Wrapper)
├ Account/Portfolio Service
├ Event Bus / Streaming Layer
├ Analytics & Back-Office Service
└ Security & Audit Module
↕
Alpaca Broker API + Market Data APIsEach service had clear responsibilities, well-defined APIs, and our code review considered edge-cases (funding delays, partial fills, currency fluctuations).
Chapter 3: Deep Dive into the Build
Here’s how specific parts came together, with code and narrative.
3.1 Setting up the Broker API Client
We prepared our wrapper around Alpaca’s Broker API. Authentication uses HTTP basic auth with API key/secret.
// config/brokerClient.ts
export const BASE_URL = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
? 'https://broker-api.alpaca.markets'
: 'https://broker-api.sandbox.alpaca.markets';
export const API_KEY = process.env.ALPACA_KEY!;
export const API_SECRET = process.env.ALPACA_SECRET!;
import axios from 'axios';
const client = axios.create({
baseURL: BASE_URL,
auth: {
username: API_KEY,
password: API_SECRET
},
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
timeout: 10000
});
export async function brokerGet(path:string, params = {}) {
return client.get(path, { params }).then(r => r.data);
}
export async function brokerPost(path:string, body:any) {
return client.post(path, body).then(r => r.data);
}3.2 Onboarding & Brokerage Account Creation
When a user signs up in the fintech app, our Onboarding Service triggers account creation with Alpaca Broker API. From their docs: you can create accounts programmatically.
export async function createBrokerAccount(user: User): Promise<string> {
const resp = await brokerPost('/v1/broker/accounts', {
alias: `user_${user.id}`,
identity: {
given_name: user.firstName,
family_name: user.lastName,
date_of_birth: user.dob,
country_of_citizenship: user.citizenship,
country_of_residence: user.residence
},
contact: {
email_address: user.email,
phone_number: user.phone,
street_address: [user.addressLine1, user.addressLine2],
city: user.city,
postal_code: user.postCode,
state: user.state
},
disclosures: {
is_control_person: false,
is_affiliated_exchange_or_finra: false
},
agreements: [
{
agreement: 'customer_agreement',
signed_at: new Date().toISOString(),
ip_address: user.signupIp
}
]
});
return resp.account_number;
}We stored the returned account_number in our internal user database, tagged the user state as “brokerage account created”, and queued the next step: bank linking.
3.3 Bank Linking & Funding Flow
We integrated a bank-link provider for UK/EU (e.g., Plaid or equivalent). When a user links their bank account, we get a processor_token, we pass it into Alpaca’s funding sources endpoint.
export async function linkBankAccount(userId: string, brokerAccount: string, processorToken: string): Promise<string> {
const resp = await brokerPost('/v1/broker/funding-sources', {
account_number: brokerAccount,
processor_token: processorToken,
user_id: userId
});
return resp.funding_source_id;
}On the UX side we made sure to show messages like “Deposit will settle in ~2-3 business days” and once cleared we changed to “Funds available to trade”. We also applied currency conversion: deposit might be £100, we log FX rate and convert underlying USD equivalent for the brokerage account.
3.4 Trading Service with Fractional Support
A critical user story: “I want to invest £50 in a U.S. stock.” That implies fractional shares, local currency, and usability. From Alpaca Broker API features: supports fractional/notional trading (buy $X amount rather than integer share).
export async function placeOrder(params: {
account_number: string;
symbol: string;
side: 'buy' | 'sell';
notionalUsd?: number;
qty?: number;
}) {
const body: any = {
account_number: params.account_number,
symbol: params.symbol,
side: params.side,
type: 'market',
time_in_force: 'day'
};
if (params.notionalUsd !== undefined) {
body.notional = params.notionalUsd;
} else if (params.qty !== undefined) {
body.qty = params.qty.toString();
}
const resp = await brokerPost('/v1/broker/orders', body);
return resp.order_id;
}We implemented a currency conversion layer:
const fxRate = await fxService.getRate('USD','GBP');
const notionalUsd = parseFloat((userInputGbp / fxRate).toFixed(2));
// then place the order
const orderId = await placeOrder({
account_number: brokerAccount,
symbol: 'AAPL',
side: 'buy',
notionalUsd: notionalUsd
});We also logged the FX rate, the user input, timestamp—so our audit trail could show exactly how many USD were sent, what FX rate was applied, and what the user saw in GBP.
3.5 Real-Time Events & Portfolio Mirror
We didn’t want users waiting for “refresh” or lag. So we implemented two mechanisms:
Webhook/Event Stream: We registered our endpoint for Alpaca events (order executed, position changed, fund settlement).
router.post('/webhooks/broker', async (req, res) => {
const ev = req.body;
await eventHandler.handleEvent(ev);
res.status(200).send('OK');
});Inside handleEvent we update order status, portfolio, and dispatch UI notifications:
async function handleEvent(ev: any) {
switch(ev.type) {
case 'order_filled':
await orderService.markFilled(ev.data);
await portfolioService.syncPosition(ev.data.account_number, ev.data.symbol);
notifyUser(ev.data.user_id, `Your order ${ev.data.order_id} is filled.`);
break;
case 'position_changed':
await portfolioService.updatePosition(ev.data);
break;
default:
logger.info(`Unhandled event type: ${ev.type}`);
}
}Periodic Reconciliation: Every 5 minutes we trigger a sync job to fetch the full list of positions from Alpaca and compare with our mirror DB—to catch any missed events, ensure consistency.
async function reconcile(accountNumber: string, userCurrency: 'GBP'|'EUR') {
const positions = await brokerGet(`/v1/broker/accounts/${accountNumber}/positions`);
for(const pos of positions) {
const marketValueUsd = parseFloat(pos.market_value);
const fx = await fxService.getRate('USD', userCurrency);
const valueLocal = marketValueUsd * fx;
await db.upsertPosition({
userId: pos.user_id,
symbol: pos.symbol,
qty: pos.qty,
valueUsd: marketValueUsd,
valueLocal: valueLocal,
currency: userCurrency
});
}
}This dual-path approach (events + reconciliation) became our reliability backbone: real-time UX plus integrity guarantees.
3.6 Monitoring, Errors & Resilience
We designed with production readiness in mind.
Latency monitoring: We tracked order submission → execution confirmation, aiming for under 2 seconds for typical market orders.
Error-tracking: We logged API errors, broker downtime, event-bus backlog. If queue depth > 1000 or error rate > 0.2 % we triggered alerts.
Retry logic: For broker API 5xx or network errors we implemented exponential back-off, up to 3 retries. We used idempotency keys (client_order_id) so duplicate requests didn’t create double orders.
Rate-limit protection: Broker API docs note that call rates are restricted. We included a rate-limit guard in our Trading Service to queue or throttle excess user actions.
Security & audit: All sensitive keys stored in secure vaults (e.g., AWS Secrets Manager). User PII encrypted at rest. Every action (account creation, funding, trade) has audit log with correlation ID, timestamp, userID.
Compliance readiness: Because the client targets UK/EU, we designed logging, data-residency, KYC workflows, consent flows from Day 0.
Chapter 4: Launch, Learnings & Growth
4.1 Pilot Launch
We launched with an initial cohort of 1,000 users (our “canary”). Here’s what we tracked:
Order latency (tap → confirmation): ~1.5 s average.
Error rate from broker API: < 0.1 %.
Portfolio update delay: median ~3.2 s after fill.
Deposits/funding settlement: some UK bank transfers took longer than expected (~48 h) → we improved UX messaging and enhanced monitoring of funding delays.
User feedback: Some users were confused seeing “USD” values; we improved UX to show “£50 → ≈ $62 (1 GBP = 1.24 USD)”. We also introduced “FX rate at time of trade: 1.24” to increase transparency.
4.2 Scaling Up
Post-pilot we opened to full launch.
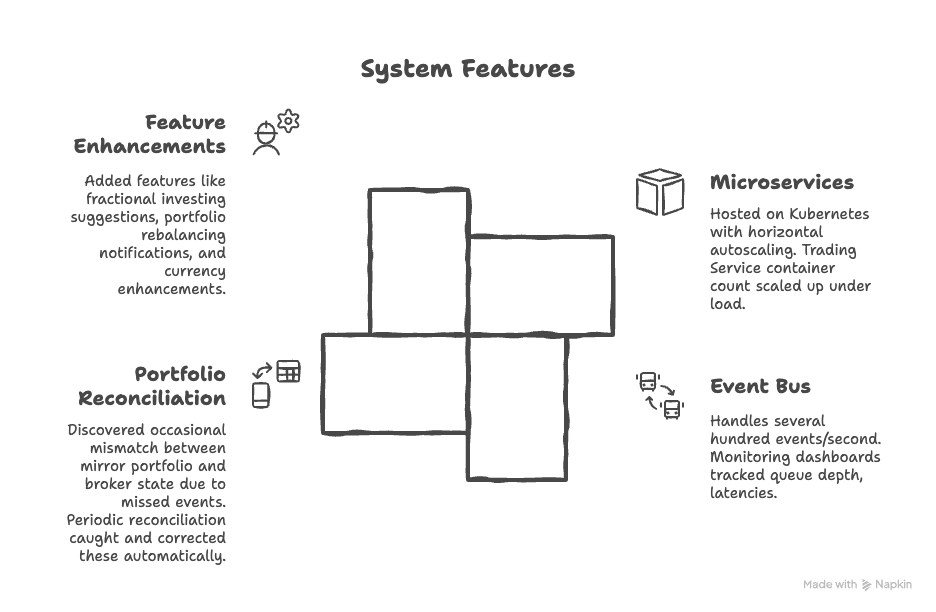
Microservices hosted on Kubernetes (AWS EKS) with horizontal autoscaling; Trading Service container count scaled up under load.
Event bus (Kafka or AWS SNS/SQS) handled several hundred events/second; monitoring dashboards tracked queue depth, latencies.
We discovered the occasional mismatch (~0.01 %) between our mirror portfolio and broker state due to missed events; our periodic reconciliation caught and corrected these automatically.
We added features like “fractional investing suggestions”, portfolio rebalancing notifications, “see your holdings in my currency” enhancements.
4.3 Future Roadmap
Even as we stabilized core features, we kept one eye on future possibilities:
Crypto trading: Alpaca Broker API supports crypto wallets and trading. We began designing a “Crypto Service” microservice, re-using our Trading Service abstraction.
Options & Fixed Income: Alpaca mentions support for options, fixed income in its roadmap. We scoped “Options Service” and “Fixed-Income Service” modules so that when we roll them out, architecture is ready.
Local-Currency Trading (LCT): Alpaca supports local-currency rails for non-USD users (i.e., deposit/trade in GBP/EUR) which we flagged for Phase 3.
Multi-broker fallback: Because we built the broker wrapper abstraction, we started a proof-of-concept with a secondary broker to reduce risk of single-rail dependency.
White-label model: Because our microservices stack was decoupled and reusable, we began discussions with the client about white-labelling the investing module for other fintech partnerships.
Chapter 5: What We Learned & Why It Matters
Lessons from the field
Brokerage rails help—but orchestration matters: Choosing a partner like Alpaca gave us the core infrastructure—but full product delivery still required careful integration (currency logic, UI/UX, error-flows, events).
Fractional shares unlock access: Allowing users to invest small amounts via notional orders is a game-changer for access and growth.
Currency clarity is key for non-USD users: Users feel safer when they understand “£50 → $X”, when FX rate is transparent, when UI shows local currency values.
Events + reconciliation ≠ optional—they’re required: Webhooks/events give speed, but periodic reconciliation catches drift and ensures integrity.
Future-proof architecture pays dividends: By building a wrapper and abstraction layer, we avoided being locked in and enabled future expansions (crypto, options, multi-broker).
Growth and tech are twin levers: For a fintech platform, delivering the rails fast matters for growth; but tech resilience and compliance matter for trust and scaling.
Strategic Implications for INSART
This project becomes a template for future fintech integrations: embedded investing module delivered in months, architecture designed for scale.
For us as Growth + Tech at INSART, we now have a real case we can present to new clients: “We’ve done this. We integrated broker-rails, built the stack, scaled to production.”
We also built IP: our microservices layer, currency conversion logic, event-bus design, broker-wrapper abstraction become reusable components across client engagements.
This engagement aligns with our ambition to be more than a digital agency—INSART positions as a fintech enabler and growth partner.
Chapter 6: Final Thoughts
Putting it all together: We helped our client transform an idea—“let everyday people invest in U.S. markets easily”—into a live, user-facing product with real trades, real outcomes. We used Alpaca Broker API to power the underlying brokerage rails, but the value came from how we integrated it: microservices architecture, currency conversion, user-experience flows, real-time events, monitoring, future-proofing.
For fintechs reading this: the path is no longer “build everything from scratch.” You can responsibly embed investing, deliver delightful UX, scale globally—provided you pick the right partner rails and build the engineering architecture and growth model around them. For INSART and for you, the message is clear: if you want to add investing to your product, you don’t need to become a broker. You need to pick your infra wisely and build experience, reliability and scale.
If you’d like to dive further – into sequence diagrams, full API maps, error-handling decision trees, or front-end UX flows – INSART is ready to deliver. Because the rails are now proven, the future is yours.